Hayatta en önemli şeylerden birisi olan sağlığımıza iyi bakmak için çabalasak da bazen genetik ve çevresel faktörler sebebiyle sağlığımızda bozulmalarla karşılaşabiliyoruz. Sağlığın bozulmasının söz konusu olduğunda ise bir takım belirtiler ortaya çıkarak hem sosyal hem de psikolojik durumumuz da olumsuz yönde etkilenebiliyor. İshal veya kramp gibi problemler kişiyi aniden etkileyebildiği için olur olmadık yerde bu problemlerin yaşanması ister istemez sinir sistemini de gerebiliyor. Planlarını iptal etmek zorunda kalan bağırsak hastaları ise bu saydığımız semptomlara bir örnek olarak karşımıza çıkıyor. Bağırsakta yara ve diğer bağırsaklardaki hastalıklar sebebiyle kişiler doktora gitmeye çekindikleri için tedaviyi de geciktiriyorlar. Dr. Meral Sözen’den bağırsakta yara nedir, bağırsakta yara oluşumunun çeşitleri, belirtileri ve sebepleri nelerdir, bağırsakta yara oluşması nasıl tedavi edilir gibi birçok sorunun yanıtını bu yazıda alabilecek ve bağırsakta yara şikâyetine başka bir perspektiften yaklaşımı edineceksiniz.
Bağırsakta Yara Nedir?
Vücudumuzda farklı zamanlarda ve koşullarda oluşan yaralar, bizlere birçok şeyin haberini verebilir. Yara oluşumları birçok sebepten ötürü “tehlikeli” sayılabilen olgular olduğu için mutlaka üstüne düşülmelidir. Bağırsakta yara oluşumları da “vücuttaki yara oluşumları” arasında en sık görülen oluşumlar olur eğer ki böyle bir durum söz konusu ise çevresel ve kalıtsal faktörlerin uzman doktorlar tarafından değerlendirilmesi sağlanmalıdır.
İnce bağırsak ya da kalın bağırsakta yara oluşumu, günümüzde sıkça görülmektedir. Sindirim sisteminde yaşanan en ufak bir problemde bağırsak bakterileri yabancı bakterilere saldırır ve hemen olası enfeksiyon vb. gibi durumları engellemek için çabalar. Ancak, normal dışı seyir etmeye başlayan bağırsak bakterileri, iyi bakterileri de öldürdüğü için enfeksiyon vb. gibi duruma bağırsakları açık hale getirir. Bağırsakta oluşan birçok sebepten ötürü bağırsak duvarı da geçirgenliğini yitirebilir ve dokusu zayıflayabilir. Bu dokunun zayıflaması ise zamanla yaraya dönüşecek ve bağırsakta yara olarak ortaya çıkacaktır.
Bağırsakta Yara Oluşumu Çeşitleri Nelerdir?
İnce bağırsakta ve kalın bağırsakta oluşabilen bağırsak yaralarının belirtileri, nedenleri ve elbette sonuçları da birbirinden farklı olacaktır. İşte, bağırsak yaralarının ayrımı;
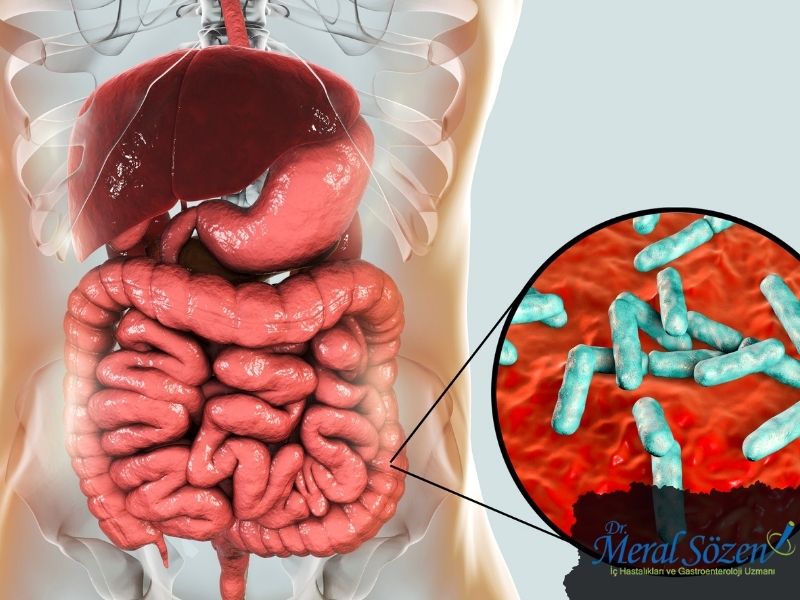
İnce Bağırsakta Yara Oluşması
Çok sık karşılaşılabilen bir durum olmamasına rağmen ince bağırsakta yara oluşumu görülebilir. Ağrıların şiddetli oluşu, ince bağırsakta yara oluşması düşüncesini akla getirebilir. Bağırsak bölgesinde oluşan ince bağırsakta yara oluşumu gençlerde yâda çocuklarda çok az görülür. 40 yaş üstü görülmesi beklenen ince bağırsakta yara oluşumu, belirli bir hastalık sonucunda da oluşabilmektedir.
Sancının varlığının alevlenmesini ardından kişide yaşanılan sorunu tespit etmek amacıyla tıbbi görüntüleme cihazları kullanılır ve net bir teşhis koyulur.
Kalın Bağırsakta Yara Oluşumu
Vücudun sindirim sisteminin bir parçası olan kalın bağırsak, ince bağırsaktan emilmek suretiyle gelen içecek ve yiyeceklerin son kez emilmesi ve anüsten dışarı atılmasından sorumludur. 180 cm uzunluğunda olan kalın bağırsağın alt kısmına rektum adı verilmektedir. Rektumda değişik hücreler bulunur ve bu hücrelerin hepsi sabittir. Eğer ki, rektumda ve kolonda bulunan bu “değişik” hücreler çoğalmaya başlarsa “UR” dediğimiz dokular oluşacaktır. Zararlı yâda zararsız olarak değişebilen bu urların çevredeki organlara sıçraması ihtimali vardır. Bu nedenle, kalın bağırsakta yara oluşumu, sebep olduğu semptomların haricinde de diğer organların sağlığı için oldukça önemli bir konudur.
Bağırsakta Yara Oluşumu Belirtileri Nelerdir?
Normal bir yara oluşumu dahi birçok olumsuz duruma yol açarken, bağırsakta yara oluşumunun elbette daha çok “etkin/ önemli” belirtileri olacaktır. Bağırsaklarda yara oluşumunun en yaygın belirtisi iltihaptır. Mide bulantısı, yüksek ateş ve kusma gibi birçok belirtinin yer aldığı bağırsakta yara şikâyetleri, kişiden kişiye de değişiklik gösterebilir.
Dışkıda görülen kan, herkesi korkutur ve akla kötü senaryolar getirir. Kimi zaman tuvalet deliğinde rastlanılan kan, bazen de dışkının iç kısmında yer alabilir ve bu gizli kanama olarak seyredebilir.
Bağırsak yara oluşumunun sonuçları ise; o bölgeden oluşan kan kayıpları nedeniyle demir eksikliği ve buna bağlı kansızlık olacaktır. Bu da bağırsakta yara oluşumunu daha da ilerletecektir.
Bağırsakta Yara Oluşumunun Tedavisi Nasıl Yapılır?
Yaranın bağırsağın hangi bölgesinde olduğuna göre bağırsak yarasının tedavisi değişmektedir. Antiasidler, proton pompa inhibitörleri, kortikosteroidler, aminosalisilatlar, antibiyotikler ve sükralfat adlı ilaç tedavileri bu hastalarda uygulanabilir. Bunun yanında mutlaka diyet önerileri ve kaçınılması gereken durumlar açısından doktorunuz sizi bilgilendirecektir. Bunun yanı sıra bu yaraların oluşmasına sebeb olan faktörlerin tedavisi ve yara oluşumundan dolayı gelişen vitamin ve mineral eksikliklerinin tedavisi de mutlaka uygulanmalıdır.





